Nanoparticle-based multifunctional therapy for Alzheimer’s developed
Nanoparticle-based multifunctional therapy for Alzheimer’s developed
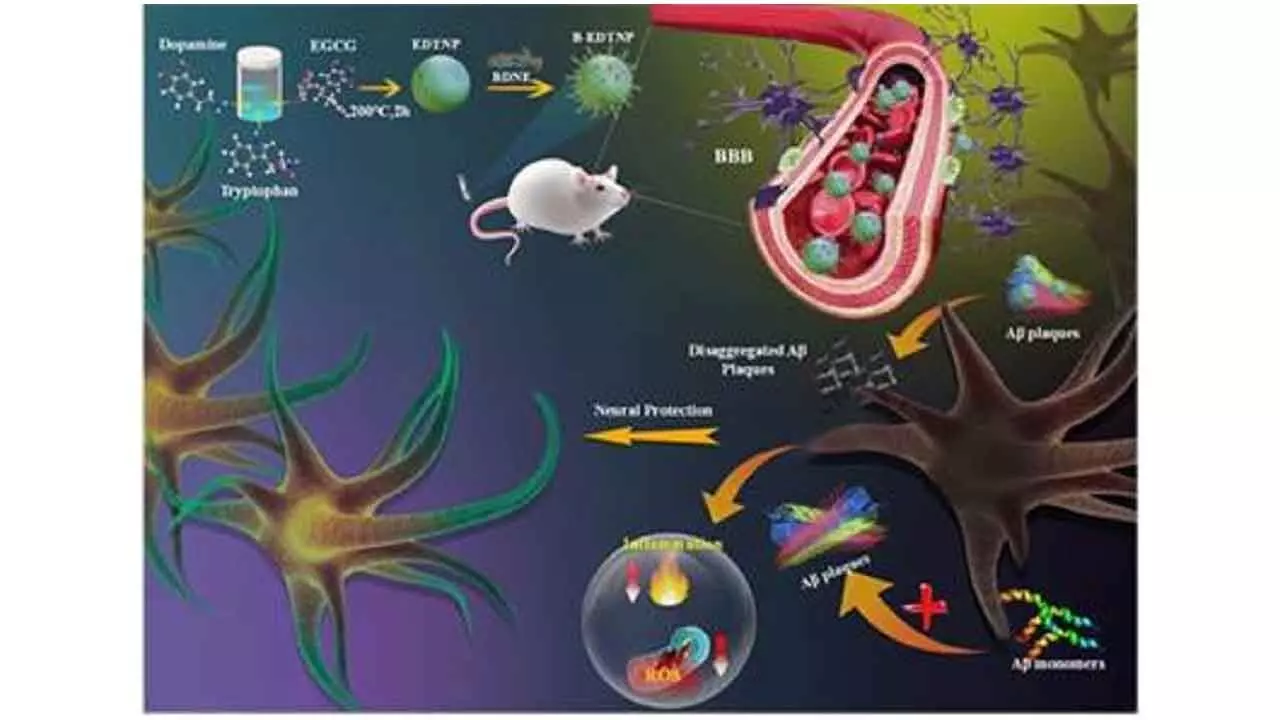
Researchers at the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, have identified a new pathway involving nanoparticles to treat Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), said the Ministry of Science & Technology.
Conventional Alzheimer’s therapies often target only a single pathological feature, such as amyloid aggregation or oxidative stress, yielding limited clinical benefit.
However, the new therapy involves nanoparticles that integrate polyphenol with antioxidant properties found in green tea, a neurotransmitter, and an amino acid.
It has the potential to treat Alzheimer’s Disease by changing the path of the progression of the disease, slowing it, improving memory, and supporting thinking skills, said the researchers in the paper, published in the journal Small.
The therapy works by integrating epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) -- an antioxidant found in green tea --, dopamine -- a neurotransmitter important for mood -- and tryptophan -- an amino acid involved in many cellular functions -- into a nanoparticle called EGCG-dopamine-tryptophan nanoparticles (EDTNPs).
This enables it to simultaneously target amyloid aggregation, oxidative stress, inflammation, and neuronal degeneration -- four key pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s.

